Future Research
Invest In Our Projects
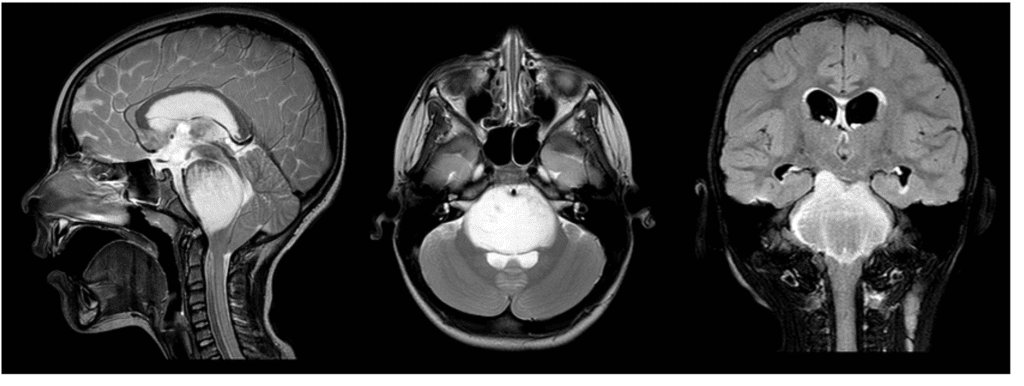
The IL13RA2-HAS2 axis as therapeutic co-targets in DIPG: $249,000 over 2 years
Be the sponsor for this project! We have investigated presence of the IL13RA2 protein in DIPG, and we have shown there is 13 times higher expression of IL13RA2 in DIPG cells versus normal cancer cells. We have also shown IL13RA2 is highly expressed at the protein level across multiple DIPG samples from cancer patients, confirming
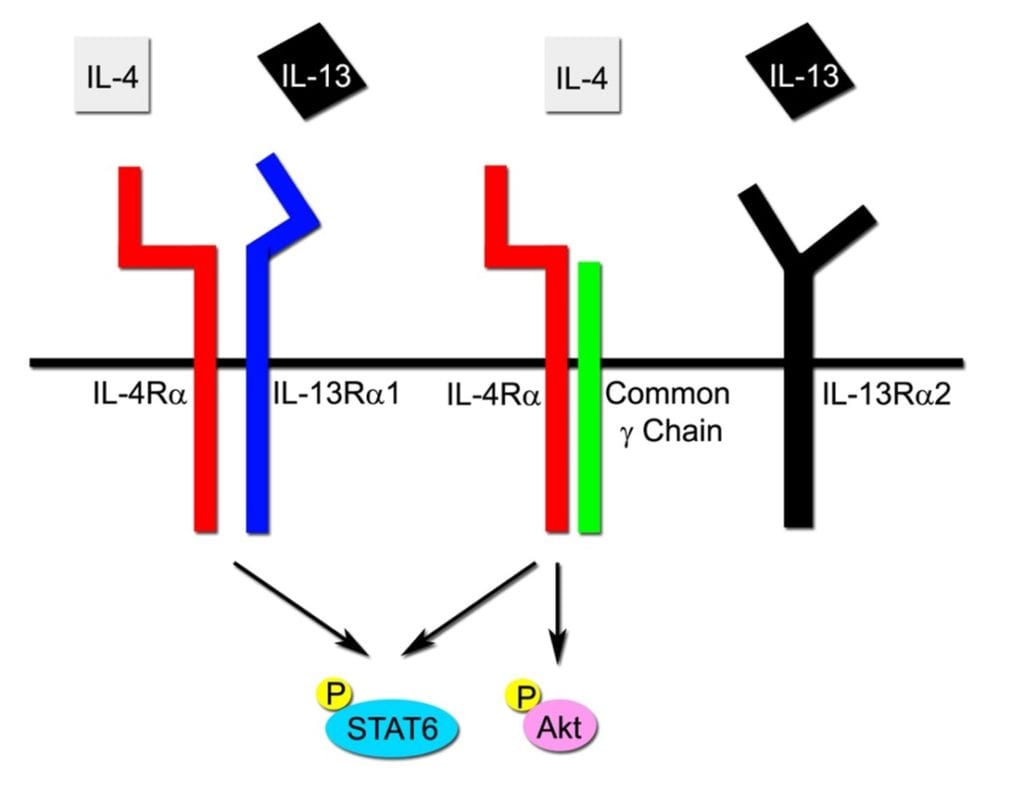
Dupixent as an anti-metastasis agent for Rhabdomyosarcoma: $240,000 over 2 years
Be the sponsor of this project! What if an FDA-approved dermatitis and asthma medicine could stop rhabdomyosarcoma metastasis? The major goal of this project is to test the hypothesis that IL4Rα blockade will prevent new soft tissue sarcoma engraftment, metastases and relapse by interfering with tumor cell – muscle stem cell interactions and thus represent
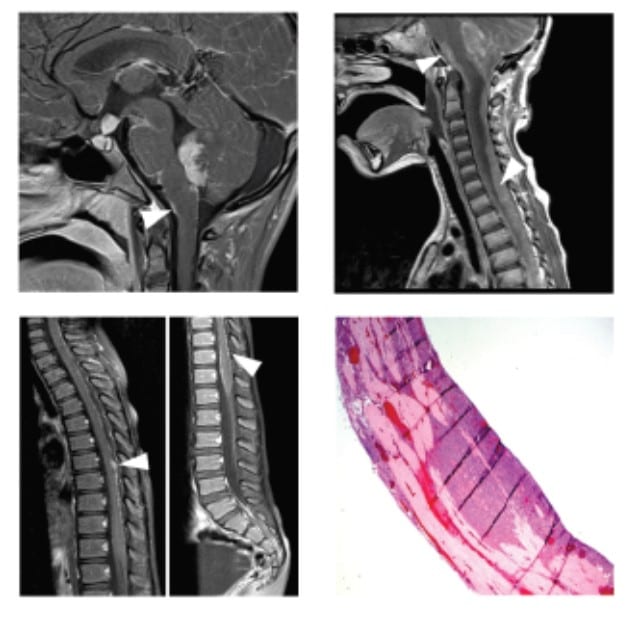
Marizomib in Medulloblastoma: $240,000 over 2 years
The goal of this preclinical study is to validate marizomib as a treatment for medulloblastoma.

CureFast: Creating a Legacy by Accelerating Childhood Cancer Research: $156,000 annually
Be the sponsor of this project! One in 5 children with cancer will not survive. We propose to address gaps in basic and translational research by improving model systems for pediatric diseases. To this end, we have developed a Legacy Gift (research autopsy) program called the Cancer Registry for Familial and Sporadic Tumors (CUREfast) to
A Radiation Synthetic Combination for Osteosarcoma Local Control: $100,000 annually
Be the sponsor of this project! Osteosarcoma is a disease for which local control can be critical: for tumors in a limb, local control permits limb-sparing procedures; whereas for tumors not in a limb, local control can mean the difference between cure and progression of disease. Our recent published studies suggest that a non-chemotherapy medicine


The IL13RA2-HAS2 axis as therapeutic co-targets in DIPG: $249,000 over 2 years
Be the sponsor for this project! We have investigated presence of the IL13RA2 protein in DIPG, and we have shown there is 13 times higher expression of IL13RA2 in DIPG cells versus normal cancer cells. We have also shown IL13RA2 is highly expressed at the protein level across multiple DIPG samples from cancer patients, confirming

Dupixent as an anti-metastasis agent for Rhabdomyosarcoma: $240,000 over 2 years
Be the sponsor of this project! What if an FDA-approved dermatitis and asthma medicine could stop rhabdomyosarcoma metastasis? The major goal of this project is to test the hypothesis that IL4Rα blockade will prevent new soft tissue sarcoma engraftment, metastases and relapse by interfering with tumor cell – muscle stem cell interactions and thus represent

Marizomib in Medulloblastoma: $240,000 over 2 years
The goal of this preclinical study is to validate marizomib as a treatment for medulloblastoma.

CureFast: Creating a Legacy by Accelerating Childhood Cancer Research: $156,000 annually
Be the sponsor of this project! One in 5 children with cancer will not survive. We propose to address gaps in basic and translational research by improving model systems for pediatric diseases. To this end, we have developed a Legacy Gift (research autopsy) program called the Cancer Registry for Familial and Sporadic Tumors (CUREfast) to

A Radiation Synthetic Combination for Osteosarcoma Local Control: $100,000 annually
Be the sponsor of this project! Osteosarcoma is a disease for which local control can be critical: for tumors in a limb, local control permits limb-sparing procedures; whereas for tumors not in a limb, local control can mean the difference between cure and progression of disease. Our recent published studies suggest that a non-chemotherapy medicine


